ApoorvCTF
Had so much fun during the CTF, really surprised with the unique categories that they brought in. We had Hardware, AI, Network and so on. Props to the organizers.
1
Author: Abu
Network
Nobita’s Network Nightmare
Description:
Nobita was given a simple task: update the company’s internal network drive. It stored important files that everyone needed. He didn’t understand much about networks, but he wanted to prove he could handle it.
Without checking the instructions, he pressed a few buttons and messed the network up. The shared ftp drive disappeared. Within minutes, employees started complaining.
Gian and Suneo, who relied on the files, stormed into the IT room. “What did you do?” they demanded. Nobita panicked and called Dekisugi.
Help Dekisugi fix the network!
Author: hampter & NotAProton
1
nc chals2.apoorvctf.xyz 3000
Given: map.pkt
Use the following link to download Cisco Packet Tracer.
Resource Hub: Get Packet Tracer, Virtual Machines, and More
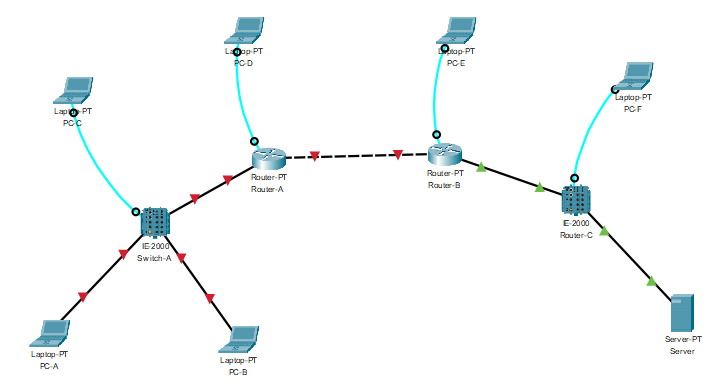
Opening up with Packet Tracer.
Reconnaissance
Immediately we can notice the connections between [Router A and B] and [Switch A to PC A and B] are down, so those might need fixing. Hovering over of the devices, we can also see the Interfaces and device details in a compact manner, giving an idea of which interfaces we need fixing. Also, mentioning the physical location is pretty cool, gives it a real life type vibes!
PC-A- IP - 178.34.23.9
- Subnet Mask - 255.255.0.0
PC-B- IP - 142.72.23.3
- No IP set for PC-C,D,E,F
Server[FTP]- IP - 192.168.1.5
- Subnet Mask - 255.255.255.0
- Default Gateway - 192.168.1.10
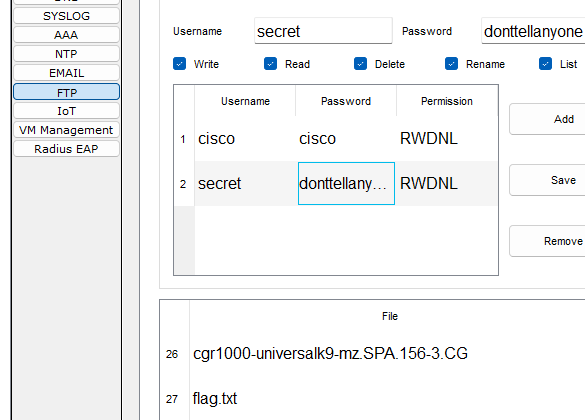
- In here, going on to the services tab we see a list of services and some random files, but we notice something important.
FTP credentials, which we can use to connect to the server after fixing the network. Also, note the flag.txt amongst the files, which we’ll eventually retrieve.
1
2
username: secret
password: donttellanyone
Switch-A- Model: IE-2000
- No IP assigned and all ports and interfaces are down.
Router-A- Model: Router-PT
- FastEthernet1/0 port has been assigned IP and subnet mask but port is still down.
- IP - 10.45.23.23
- Subnet Mask - 255.0.0.0
Router-B- Model: Router-PT
- Same as Router-A but FastEthernet1/0 is up!
- IP - 192.168.1.10
- Subnet Mask - 255.255.255.0
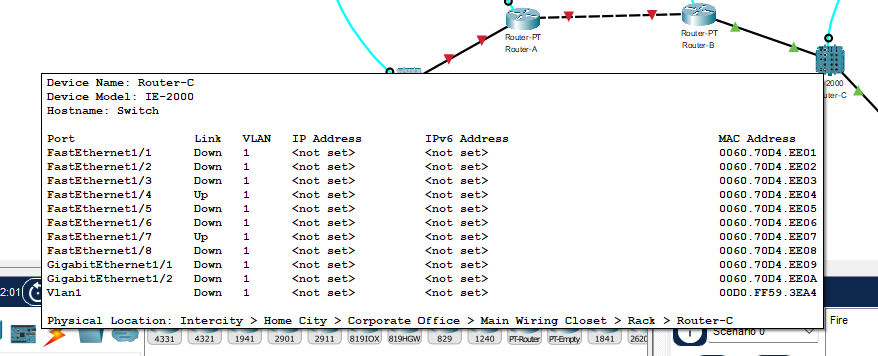
Router-C- Model:
IE-2000 - No IP assigned, but both FastEthernet1/4 and FastEthernet1/7 ports are up!
- Model:
Prerequisites
Recap for both the author and the reader. Skip if you big brain.
An interface is a connection point between a device and a network. Every networking device (routers, switches, PCs) has interfaces that allow them to send and receive data.
- On a PC, the interface is usually a Network Interface Card (NIC), which connects to an Ethernet port or Wi-Fi.
- On Routers and Switches, interfaces are typically Ethernet ports (e.g.,
FastEthernet,GigabitEthernet, orSerialfor WAN connections).
In Cisco Packet Tracer, network interfaces are named in a format like:
1
2
3
FastEthernet1/1
GigabitEthernet0/0
Serial2/0
Let’s break it down:
- FastEthernet / GigabitEthernet → The interface type.
FastEthernetis 100 Mbps,GigabitEthernetis 1 Gbps. - 1/1 →
- The first number (
1) refers to the module slot on the device. - The second number (
1) refers to the port number on that module.
- The first number (
If you see FastEthernet1/4, it means:
- It’s a FastEthernet (100 Mbps) port.
- It’s in module 1 of the device.
- It’s the 4th port in that module.
In Packet Tracer, when configuring a switch or router, you enable/disable these interfaces to control network connectivity.
Solution
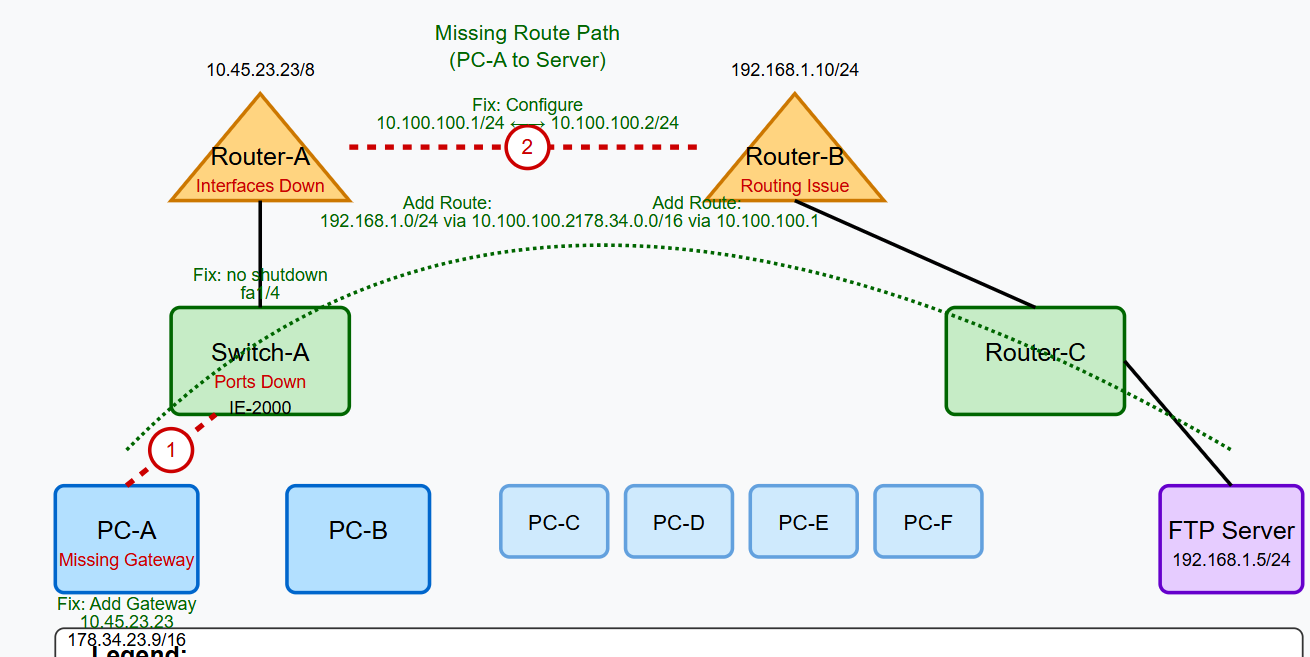
Now that we identified all devices, interfaces that are down, and other configurations we can get to the solving part.
Configure Switch-A to enable PC-A's connection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
3 # Select Switch-A
enable # Enter privileged EXEC mode (administrative access)
configure terminal # Enter global configuration mode
interface fa1/4 # Select the FastEthernet port connected to PC-A
no shutdown # Enable the port (remove the shutdown state)
exit # Exit interface configuration mode
exit # Exit global configuration mode
exit # Return to device selection menu
Explanation: Switches operate at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of the OSI model. Their primary job is to forward frames between devices on the same network. The no shutdown command is crucial because it physically enables the port, allowing data to flow through it. Without this step, even with correct IP configurations, no data can pass through a shutdown port.
Configure Router-A to enable Router-B's connection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
4 # Select Router-A
enable # Enter privileged EXEC mode
configure terminal # Enter global configuration mode
interface fa1/0 # Select the interface that was down
no shutdown # Enable the interface
exit # Exit interface configuration mode
interface fa0/0 # Select the interface that will connect to Router-B
ip address 10.100.100.1 255.255.255.0 # Configure IP address and subnet mask
no shutdown # Enable the interface
exit # Exit interface configuration mode
ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.100.100.2 # Add static route to the server network
exit # Return to device selection menu
Explanation: Routers operate at Layer 3 (Network Layer) of the OSI model and route packets between different networks. Here we’re doing three critical things:
- Enabling the existing interface (fa1/0) that was down
- Configuring a new IP address on fa0/0 (10.100.100.1) to create a subnet with Router-B
- Adding a static route that tells Router-A: “To reach the 192.168.1.0/24 network (where the FTP server lives), send packets to Router-B (10.100.100.2)”
Configure Router-B to route back to Router-A's network
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
5 # Select Router-B
enable # Enter privileged EXEC mode
configure terminal # Enter global configuration mode
interface fa0/0 # Select the interface connected to Router-A
ip address 10.100.100.2 255.255.255.0 # Configure IP address and subnet mask
no shutdown # Enable the interface
exit # Exit interface configuration mode
ip route 178.34.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.100.100.1 # Add static route to PC-A's network
exit # Return to device selection menu
Explanation: This step mirrors what we did for Router-A, but in the reverse direction:
- We’re configuring Router-B’s interface with IP 10.100.100.2 (the other end of the link to Router-A)
- Adding a static route that tells Router-B: “To reach the 178.34.0.0/16 network (where PC-A lives), send packets to Router-A (10.100.100.1)”
This completes the two-way routing path needed for traffic to flow in both directions.
Configure PC-A and retrieve the flag
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
1 # Select PC-A
ipconfig 178.34.23.9 255.255.0.0 10.45.23.23 # Set IP, subnet, and default gateway
ping 192.168.1.5 # Test connectivity to the FTP server
ftp 192.168.1.5 # Connect to the FTP server
secret # Enter username
donttellanyone # Enter password
get flag.txt # Download the flag file
quit # Exit FTP
cat flag.txt # Display the contents of the flag file
Explanation: Now we configure PC-A with its default gateway (Router-A’s IP address), which tells PC-A where to send packets destined for other networks. Then we test connectivity with ping, and finally use FTP to retrieve the flag file.
Really cool challenge as it’s one of it’s kind. By the way, if you’re too lazy to type these all out, just run the following code. Just run it twice if it lags.
1
curl -L https://gist.github.com/AbuCTF/6f17f8c9395be91dfdefff285f1a1d34/raw | python3
Flag: apoorvctf{N0bit4s_ju5t_un1ucky}
Infrastructure
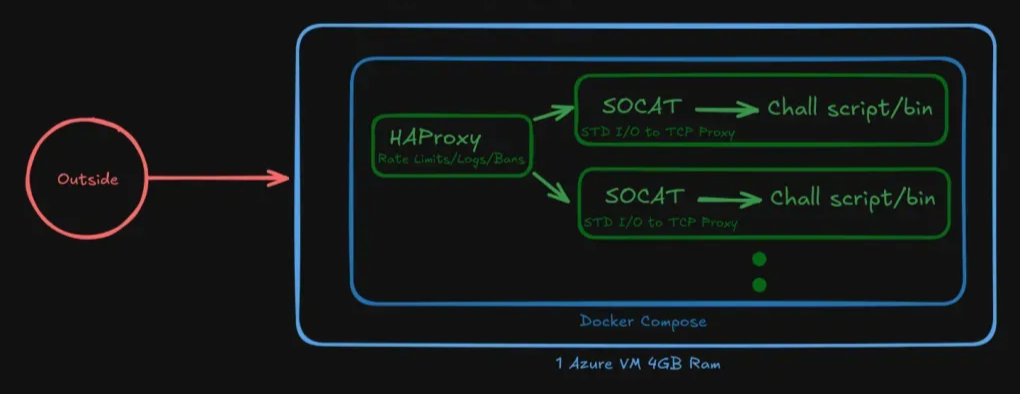
I talked to the author and here’s how the chals2.apoorvctf.xyz were hosted. As for the networking challenge, it was a Python CLI simulator which Socat served over TCP, HaProxy in front for logs/rate-limiting, all built on an Azure VM. Cool stuff!
Will be back!